Neuromarketing Branding Guide

Traditional marketing strategies often miss the mark. Neuromarketing offers a scientific approach, allowing brands to connect with consumers on a deeper, subconscious level and build lasting loyalty.
This guide explores the core principles of neuromarketing and its application in branding. We will delve into emotional triggers, sensory design, cognitive biases, and mirror neurons, providing actionable insights and real-world examples to help you create more effective and memorable brand experiences that drive growth.
What Is Neuromarketing? A Deep Dive into the Science of Branding
In a world saturated with advertising, getting a consumer’s attention is only the first, and perhaps easiest, challenge. The real goal is to create a lasting impression—a connection that translates into brand loyalty. This is where neuromarketing emerges as a game-changing discipline. At its core, neuromarketing is the application of neuroscience to marketing. It bridges the gap between consumer psychology and data-driven marketing, seeking to understand the “why” behind consumer choices.
Traditional market research methods like surveys and focus groups are valuable, but they have a significant limitation: they rely on what consumers say they think and feel. Humans are not always reliable narrators of their own subconscious motivations. We rationalize decisions, misremember feelings, or simply say what we think the researcher wants to hear. Neuromarketing bypasses this conscious filter. It uses scientific tools to measure what is happening in the brain and body in real-time as a consumer interacts with a brand.
The Toolkit of Neuromarketing
To peer into the consumer brain, neuromarketing experts use a variety of advanced technologies. Understanding these tools helps clarify how neuromarketing generates its powerful insights:
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): This technology measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. When a specific area of the brain is active, it requires more oxygen, and the fMRI can pinpoint these “hot spots.” While incredibly precise, fMRI machines are expensive and require subjects to lie still, making them less common for large-scale neuromarketing studies.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG is a more common and portable tool in neuromarketing. It uses a cap of electrodes placed on the scalp to measure electrical activity in the brain. It can track engagement, emotional arousal, and cognitive load in real-time, making it ideal for testing video ads, websites, and packaging designs.
- Eye-Tracking: This technology follows where a person is looking, for how long, and in what order. Eye-tracking glasses or screen-based trackers reveal which parts of an ad, website, or store shelf are most visually engaging and which are ignored. It’s a cornerstone of user experience (UX) design and a key part of neuromarketing.
- Facial Coding: By analyzing subtle facial expressions using a webcam, facial coding software can decode a person’s emotional response (e.g., happiness, surprise, confusion, disgust). This provides a moment-by-moment emotional journey as a user interacts with content.
- Biometrics: This category includes measuring physiological responses like heart rate, skin conductivity (GSR), and respiration. These metrics indicate emotional arousal and engagement levels, providing another layer of data for neuromarketing analysis.
By combining these technologies, neuromarketing provides a holistic, unbiased view of the consumer experience. It’s not about manipulating people; it’s about understanding them on a profound level to create better products, more intuitive websites, and more resonant brand stories.
Emotional Triggers: The Heart of Memorable Branding

Emotion is the most powerful force in branding. We don’t remember facts and figures; we remember how things make us feel. This isn’t just a poetic notion—it’s a biological fact, and it’s a central pillar of neuromarketing. The brain’s emotional center, the limbic system, is deeply intertwined with its memory center.
The Amygdala and Hippocampus: A Powerful Partnership
The amygdala is the brain’s emotional watchdog. It processes emotions like joy, fear, surprise, and anger. When you experience a strong emotion, your amygdala goes into high alert. This activation sends a signal to the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for forming long-term memories. The message is simple: “This is important. Remember it.”
This is why your most vivid memories are often tied to strong emotions—your first love, a major achievement, or a frightening event. Effective neuromarketing aims to create these “emotional tags” for a brand. When an ad makes you laugh, a story makes you feel inspired, or a customer service experience makes you feel valued, your brain is more likely to encode that brand into your long-term memory. This is the essence of emotional marketing.
Crafting Emotional Brand Stories
Brand storytelling is one of the most effective ways to leverage emotional triggers. A good story does more than just list product features; it creates a narrative with characters, conflict, and resolution that the audience can connect with emotionally.
- The Hero’s Journey: Position your customer as the hero of the story and your brand as the mentor or magical tool that helps them overcome a challenge. Nike is a master of this, using athletes’ stories of struggle and triumph to inspire us.
- Nostalgia: Tapping into positive memories from the past is a powerful emotional trigger. Brands like Coca-Cola and McDonald’s often use nostalgic imagery and music to evoke feelings of warmth and comfort.
- Surprise and Delight: Unexpected positive experiences create a strong emotional peak. A surprise gift with purchase, a witty and unexpected social media reply, or an exceptionally beautiful unboxing experience all use this neuromarketing principle.
- Empathy: Showcasing stories that allow the audience to feel what another person is feeling can create a powerful bond. Charities excel at this, but commercial brands like Dove (with its “Real Beauty” campaigns) have also used empathy to build immense brand equity.
By focusing on emotion, neuromarketing helps brands move from being a simple choice to becoming a meaningful part of a consumer’s life.
The Power of Sensory Branding: Engaging More Than Just the Eyes
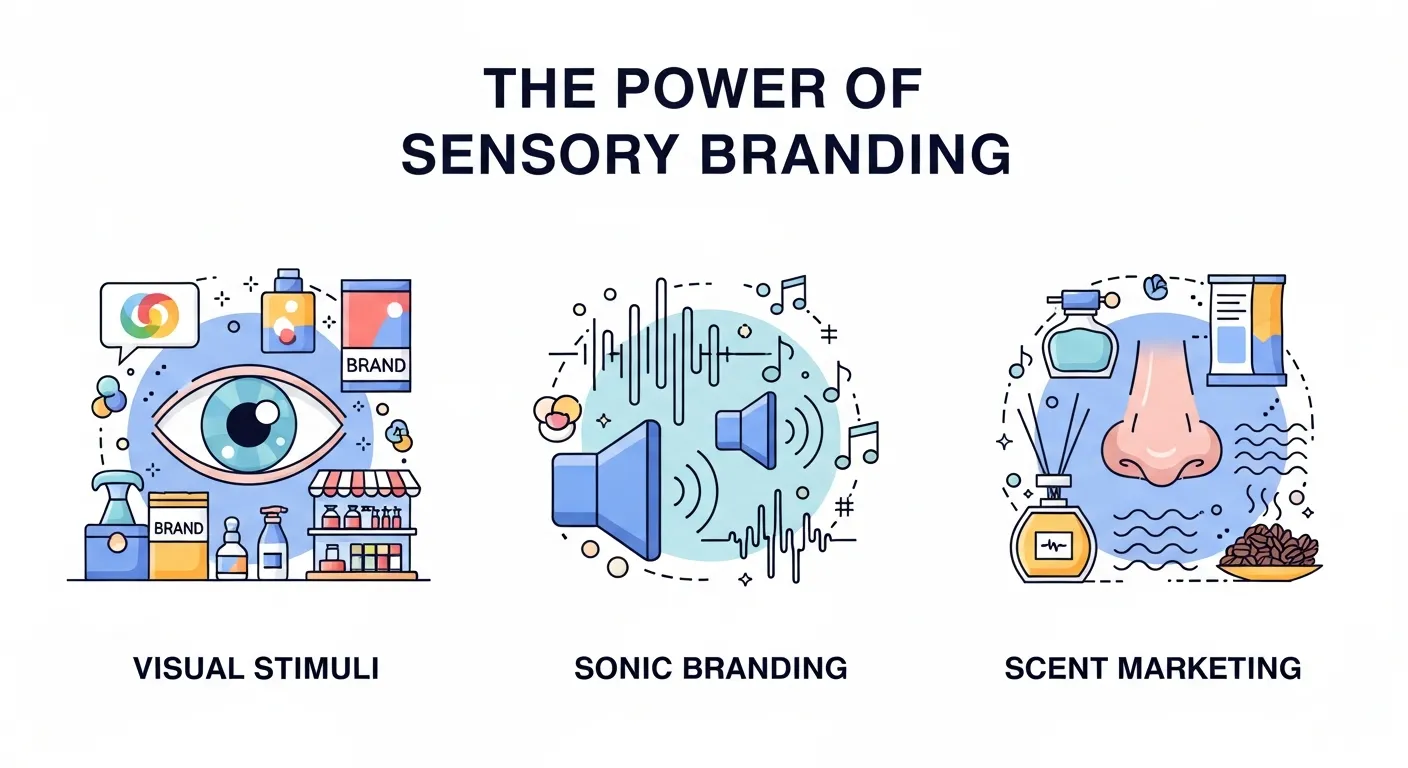
While vision is our dominant sense, our experience of the world is multisensory. The most powerful brand experiences are those that engage multiple senses to create a rich, immersive world. This is the domain of sensory branding, a key application of neuromarketing. Each sense provides a different pathway to the brain, and engaging them in concert creates a stronger, more memorable brand impression.
Visual Stimuli: The 60,000x Advantage
Our brains process images about 60,000 times faster than text. Visuals are the foundation of branding, and neuromarketing provides a scientific lens through which to optimize them.
- Color Psychology: Colors evoke specific emotions and associations. Blue conveys trust and security (used by banks and tech companies), red signifies excitement and urgency (used for sales and fast food), and green communicates nature, health, and growth.
- Shape & Form: The brain prefers rounded, curved shapes over sharp, angular ones. Apple’s product design, with its soft curves and smooth edges, is a textbook example of using this neuromarketing principle to create products that feel friendly and approachable.
- Simplicity vs. Complexity: Our brains are wired to conserve energy. A simple, clean design (like Google’s homepage) reduces cognitive load and is processed more easily and positively than a cluttered, complex one. This is a core tenet of brand simplification.
Sonic Branding: The Sound of Your Brand
Sound is a deeply emotional sense. A jingle, a specific sound effect, or even the voice of your brand can become instantly recognizable. This is sonic branding.
- Jingles & Melodies: Intel’s five-note chime or McDonald’s “I’m Lovin’ It” jingle are powerful sonic assets. They are easy to remember and trigger instant brand recognition.
- Ambient Sound: The music played in a retail store has a profound impact on shopper behavior. Fast-paced music can increase turnover in a restaurant, while slower, classical music can encourage high-end shoppers to browse longer and spend more. This is a subtle but effective neuromarketing tactic.
- Product Sounds: Even the sound a product makes is part of its brand. The “click” of a luxury car door, the “crunch” of a potato chip, or the “pop” of a cork are all carefully engineered sensory cues.
Scent Marketing: The Most Powerful Memory Trigger
Smell is the sense most directly linked to memory and emotion. The olfactory bulb has a direct line to the brain’s limbic system.
- Signature Scents: Many hotels (like Westin’s White Tea scent) and retail stores (like Abercrombie & Fitch) use a unique scent to create a memorable and consistent brand environment.
- Product Scent: The smell of a new car or the scent of freshly baked goods in a supermarket are powerful sales drivers. These scents trigger positive emotional associations.
Touch (Haptic) and Taste
The sense of touch conveys quality and value. The weight of a product, the texture of its packaging, and the feel of a fabric all contribute to brand perception. For food and beverage brands, taste is obviously paramount. Neuromarketing studies can even measure how packaging and branding influence the perceived taste of a product.
By thinking about your brand as a complete sensory experience, you can create a much deeper and more resilient connection with your customers. A consistent, multisensory approach is a hallmark of a strong brand strategy framework.
Mirror Neurons and Social Proof: The Neuroscience of “Me Too”

Humans are fundamentally social creatures. Our brains are wired to connect with, understand, and imitate others. A key part of this social wiring is a fascinating set of brain cells called mirror neurons. These neurons fire not only when we perform an action but also when we watch someone else perform that same action. They are the neural basis of empathy, and they are a powerful tool in the neuromarketing toolkit.
How Mirror Neurons Influence Behavior
When you see someone smile, your mirror neurons fire, and you subconsciously feel a glimmer of that same happiness. When you watch an athlete score a winning goal, your brain simulates the movements and the feeling of triumph. This is why watching others enjoy a product is so persuasive.
- Seeing is Feeling: A video of someone taking a refreshing sip of a cold drink on a hot day makes you feel a little more thirsty. A testimonial showing a customer’s genuine joy and relief after solving a problem with your product makes you feel that same relief. Your mirror neurons bridge the gap between their experience and your own.
- User-Generated Content (UGC): This is neuromarketing gold. When potential customers see photos and videos of real, relatable people using and loving your product, their mirror neurons go to work. It’s far more persuasive than a polished ad with paid actors because it feels more authentic.
- Influencer Marketing: A major reason influencer marketing services are so effective is because they leverage mirror neurons. Followers feel a sense of connection and trust with the influencer. When the influencer enthusiastically uses a product, that feeling is vicariously transferred to the audience.
The Power of Social Proof
Mirror neurons are closely linked to the psychological principle of social proof. This is the idea that we look to the actions and behaviors of others to determine our own. If a restaurant is full, we assume the food is good. If a product has thousands of positive reviews, we assume it’s a safe bet.
Neuromarketing shows that social proof is a mental shortcut that reduces cognitive load. Instead of doing exhaustive research, our brain says, “If all these people like it, it’s probably good for me too.” Brands can leverage this through:
- Reviews and Ratings: Prominently displaying star ratings and customer reviews.
- Testimonials: Featuring quotes and stories from happy customers.
- “As Seen On” Logos: Showcasing logos of media outlets that have featured the brand.
- Social Media Follower Counts: Displaying the size of your community.
- Real-Time Purchase Notifications: E-commerce pop-ups that say “John from New York just bought this item.”
By strategically combining the power of mirror neurons (showing the experience) and social proof (showing the numbers), brands can create a powerful persuasive loop that encourages trust and drives conversions. It’s a fundamental part of building brand authority.
Cognitive Biases: The Brain’s Shortcuts and How They Shape Decisions
Our brains make millions of decisions every day. To cope with this immense workload, they develop mental shortcuts, or cognitive biases. These are systematic patterns of deviation from rational judgment. They are not flaws; they are efficiency mechanisms. For marketers, understanding these biases is a core part of effective neuromarketing. By ethically framing messages in a way that works with these biases, brands can communicate more persuasively.
It’s crucial to approach this with an ethical branding mindset. The goal is not to manipulate, but to communicate more clearly by understanding how the brain naturally processes information.
Key Cognitive Biases in Marketing
Table: Common Cognitive Biases and Their Marketing Applications
|
Cognitive Bias |
Description |
Neuromarketing Application |
|---|---|---|
|
Anchoring |
The tendency to rely heavily on the first piece of information offered (the “anchor”) when making decisions. |
Displaying the original price next to a sale price (“Was $100, Now $75”). The $100 acts as the anchor, making $75 seem like a great deal. |
|
Loss Aversion |
The tendency to feel the pain of a loss more strongly than the pleasure of an equal gain. |
Using scarcity and urgency. “Only 3 left in stock!” or “Offer ends in 24 hours.” This triggers the fear of missing out (Marketing FOMO). |
|
Framing Effect |
The tendency to draw different conclusions from the same information, depending on how it is presented. |
“90% fat-free” sounds healthier than “Contains 10% fat.” A “95% success rate” is more persuasive than a “5% failure rate.” |
|
Decoy Effect |
The phenomenon where consumers change their preference between two options when a third, asymmetrically dominated option is presented. |
A movie theater offers a small popcorn for $3, a large for $7. Most buy the small. Add a medium decoy for $6.50, and most will now buy the large because it seems like a better value. |
|
Bandwagon Effect |
The tendency to do or believe things because many other people do or believe the same. |
This is the mechanism behind social proof. “Join 2 million satisfied customers!” or showing trending products. |
|
IKEA Effect |
The tendency to place a disproportionately high value on products the consumer partially created. |
Brands like IKEA or meal-kit services like Blue Apron leverage this. The effort invested increases perceived value. |
|
Confirmation Bias |
The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information that confirms or supports one’s preexisting beliefs. |
Using targeted ads that align with a user’s known interests. It reinforces their sense of making a good, informed choice. |
Implementing Biases Ethically
Using these neuromarketing insights requires a delicate touch. A brand that overuses scarcity tactics or creates false urgency can quickly erode trust. The key is to use these principles to reduce friction and make the customer’s decision-making process easier.
For example, a webinar sales funnel might use loss aversion by highlighting that “replay will only be available for 48 hours.” This is an ethical use if it’s true and helps people prioritize watching valuable content. However, creating a fake countdown timer that resets on every page refresh is deceptive and damages brand perception. A strong brand strategy guide should include ethical guidelines for applying these powerful neuromarketing principles.
Case Studies: Brands Winning with Neuromarketing

The principles of neuromarketing aren’t just theoretical. Many of the world’s leading brands have been intuitively or intentionally using brain-based strategies for years. Analyzing their success provides a practical roadmap for applying these concepts.
Apple: The Master of Simplicity and Sensory Experience
Apple is a quintessential example of a brand built on neuromarketing principles.
- Cognitive Fluency: Apple’s minimalist product design and clean user interfaces are easy on the brain. They reduce cognitive load, making the products feel intuitive and effortless to use. This aligns with the brain’s preference for simplicity.
- Sensory Branding: From the satisfying “click” of the AirPods case to the haptic feedback on the iPhone, Apple products are a masterclass in sensory design. The unboxing experience itself is a carefully choreographed ritual.
- The IKEA Effect: By encouraging users to set up their own devices and personalize them with apps and settings, Apple subtly increases the user’s sense of ownership and value.
Coca-Cola: The Architect of Emotional Association
Coca-Cola sells sugar water, but it has built an empire by selling happiness. Its brand marketing strategy is a long-term neuromarketing campaign.
- Emotional Triggers: For decades, Coke’s advertising has consistently associated the brand with positive, high-arousal emotions: joy, togetherness, celebration, and nostalgia (especially with its holiday campaigns).
- Color Psychology: The iconic “Coke Red” is a high-energy, attention-grabbing color that signals excitement.
- Mirror Neurons: Their ads are filled with smiling, happy people sharing moments together while drinking Coke, activating the viewer’s mirror neurons and creating a vicarious sense of that same joy.
Nike: The Storyteller of Triumph and Motivation
Nike’s “Just Do It” is more than a slogan; it’s a powerful command that taps into the brain’s reward and motivation centers.
- Brand Storytelling: Nike doesn’t just sell shoes; it sells the story of overcoming adversity. By featuring athletes in their moments of struggle and ultimate triumph, they create powerful emotional narratives that inspire and motivate.
- Activation of Motor Cortex: The use of dynamic, high-action visuals of athletes running, jumping, and competing literally activates the motor cortex in the viewer’s brain, creating a physical sense of energy and readiness.
- Social Proof: By aligning with the world’s top athletes, Nike creates powerful social proof. If it’s good enough for Michael Jordan or Serena Williams, the brain concludes, it’s good enough for me.
Frito-Lay: The Science of the Crunch
Even snack foods are deeply invested in neuromarketing. Frito-Lay famously conducted neuromarketing studies to optimize its products.
- Sensory Optimization: They discovered that the “crunch” sound is a huge driver of perceived freshness and enjoyment. They have engineered their chips to have the perfect auditory feedback.
- Brain-Based Packaging: Their research found that matte packaging with images of healthy ingredients elicited a more positive neural response than shiny bags, as the brain subconsciously perceived it as less “guilty.” This led to a redesign of their SunChips bags.
These digital marketing success stories show that whether you’re selling technology, beverages, apparel, or snacks, understanding the consumer brain through neuromarketing can provide a significant competitive advantage.
Implementing Neuromarketing Insights into Your Branding Strategy
You don’t need an fMRI machine or a dedicated neuroscience lab to start applying the principles of neuromarketing. Many of these powerful insights can be implemented on a practical, and even a small, budget. The key is to start thinking like a neuromarketer by focusing on the subconscious experience of your customer at every touchpoint.
Start with a Neuromarketing Audit
Begin by conducting a brand audit through a neuromarketing lens. Go through your entire customer journey mapping process and ask critical questions at each stage:
- Website/App:
-
- Visuals: Are your images emotionally resonant? Are you showing people’s faces (especially making eye contact)?
- Simplicity: Is the navigation intuitive? Is there too much text or clutter causing cognitive overload? Use heatmap tools to see where users are getting stuck.
- Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Do the colors of your CTA buttons contrast with the background? Is the language action-oriented?
- Packaging:
-
- Sensory: What is the tactile experience? Is the material pleasant to touch? Does it have a satisfying sound when opened?
- Visual Hierarchy: What is the first thing a customer’s eye is drawn to? Is it your brand logo or an important product benefit?
- Advertising (Social, Video):
-
- Emotion: Does your ad tell a story? Does it evoke a specific, strong emotion within the first 3 seconds?
- Mirror Neurons: Are you showing relatable people enjoying the benefits of your product?
- Content Marketing (Blogs, Emails):
-
- Framing: Are you framing your headlines and benefits positively? Are you using storytelling to make your points more memorable?
- Cognitive Biases: Are you using social proof (e.g., “Our most popular article”) to guide readers?
A/B Testing with a Neuromarketing Focus
A/B testing is a marketer’s best friend. By applying neuromarketing principles, you can make your tests much more strategic.
- Test Emotional Triggers: Test two versions of an ad: one that focuses on logical features and one that tells an emotional story. Measure click-through rates and conversion.
- Test Color Psychology: Test different colors for your CTA buttons. Often, a high-contrast color like orange or green will outperform a brand-aligned but low-contrast color.
- Test Anchoring: Test your pricing page layout. Does placing a higher-priced “premium” option first increase the take-rate of your “standard” option?
- Test Social Proof: Test adding customer testimonials or star ratings near a “Buy Now” button. Does it increase conversions?
Leveraging Affordable Tech
While EEG and fMRI might be out of reach, there are many affordable tools that can provide neuromarketing insights:
- Heatmap and Session Recording Tools: Services like Hotjar or Crazy Egg visually show you where users click, move, and scroll on your site. Session recordings let you watch a user’s entire journey, revealing points of friction and confusion.
- Google Analytics: This free tool is a treasure trove of data. Analyze user flow, bounce rates, and time on page to identify which content is engaging and which is causing users to leave. You can find more on this at Google Analytics.
The journey into neuromarketing is iterative. Start small, test your hypotheses, measure the results, and gradually build a repository of what works for your audience. This data-driven approach will refine your brand positioning and improve the effectiveness of every marketing dollar you spend.
Conclusion
Neuroscience-driven branding moves marketing from an art of persuasion to a science of connection. By understanding the deep-seated emotional triggers, cognitive biases, and sensory preferences of the human brain, brands can create experiences that are not just seen, but felt. This is the future of neuromarketing. Start by auditing your brand’s sensory and emotional touchpoints, test your hypotheses with a scientific mindset, and commit to building a brand that the brain will remember, trust, and love for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Neuromarketing?
Neuromarketing is an interdisciplinary field that combines neuroscience, psychology, and marketing to study and understand consumer behavior. It uses tools like EEG, fMRI, and eye-tracking to measure subconscious responses to marketing stimuli, providing insights that traditional research methods might miss.
2. How does neuromarketing differ from traditional marketing?
Traditional marketing often relies on what consumers say in surveys or focus groups. Neuromarketing measures what consumers actually feel and think on a subconscious level by observing brain activity and physiological responses. It focuses on the “why” behind consumer actions, not just the “what.”
3. What role do emotions play in a neuromarketing strategy?
Emotions are central to neuromarketing. Emotional responses trigger the release of neurotransmitters that enhance memory encoding, making a brand or message more memorable. A successful neuromarketing strategy focuses on creating positive emotional associations with the brand.
4. How can a small business use neuromarketing without a big budget?
Small businesses can apply neuromarketing principles by focusing on the fundamentals: using color psychology in their branding, crafting emotional stories in their content, leveraging social proof with customer reviews, A/B testing website elements to reduce cognitive load, and creating a positive sensory experience for customers.
5. What are cognitive biases, and why are they important in neuromarketing?
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts the brain uses to make decisions quickly. Neuromarketing studies these biases (like anchoring, loss aversion, and the framing effect) to understand how to present information more persuasively and make the customer’s decision-making process easier.
6. Is neuromarketing ethical?
This is a critical question. When used to better understand consumer needs and create more valuable and pleasant experiences, neuromarketing is ethical. However, if used to exploit subconscious vulnerabilities or manipulate people into making poor decisions, it becomes unethical. Responsible brands use neuromarketing to improve, not deceive.
7. What is sensory branding?
Sensory branding is a neuromarketing technique that aims to appeal to all five senses—sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste. By creating a multi-sensory brand experience, companies can forge stronger and more memorable emotional connections with their customers.
8. How are mirror neurons used in marketing?
Mirror neurons are brain cells that fire when we observe someone else’s actions. Marketers leverage this by showing relatable people enjoying a product in advertisements or testimonials. This makes the viewer vicariously experience the same positive feeling, increasing their desire for the product.
9. Can neuromarketing predict sales success?
While neuromarketing can’t predict sales with 100% certainty, it is a powerful predictive tool. Studies have shown that metrics derived from neuromarketing (like emotional engagement and memory encoding) are often better predictors of an ad’s in-market success than traditional survey-based metrics.
10. What is the future of neuromarketing?
The future of neuromarketing lies in increasing personalization and real-time adaptation. With the rise of wearable technology and AI, brands may soon be able to tailor experiences to an individual’s real-time emotional and cognitive state, creating hyper-personalized and highly effective marketing, all while navigating complex ethical considerations.






